How to operate a drone is a question many ask, and this guide provides a comprehensive answer. From understanding the various drone types and their unique operational characteristics to mastering advanced flight techniques and ensuring safe operation, we’ll cover all the essential aspects. We’ll explore pre-flight checks, legal considerations, and essential maintenance procedures, equipping you with the knowledge and confidence to take to the skies responsibly.
This guide will delve into the intricacies of drone controls, camera operation, and image capture, enabling you to produce stunning aerial photography and videography. We’ll also examine troubleshooting common issues and address safety best practices, ensuring a smooth and enjoyable experience for both novice and experienced pilots.
Drone Types and Their Operation
Understanding the different types of drones and their operational characteristics is crucial for safe and effective operation. This section will explore the variations in operation between quadcopters, hexacopters, and octocopters, compare fixed-wing and multirotor drones, and provide examples of specific drone models with unique features.
Multirotor Drone Operation Differences
Quadcopters, hexacopters, and octocopters are all multirotor drones, differing primarily in the number of rotors. This impacts their stability, payload capacity, and redundancy. Quadcopters, with four rotors, offer a good balance of simplicity and stability. Hexacopters, with six rotors, provide increased redundancy and lifting capacity, making them suitable for heavier payloads. Octocopters, with eight rotors, offer the highest redundancy and payload capacity, ideal for professional applications.
However, increased complexity comes with increased maintenance needs.
Fixed-Wing vs. Multirotor Drones
| Feature | Fixed-Wing | Multirotor |
|---|---|---|
| Flight Time | Longer flight times due to efficient aerodynamics. | Shorter flight times due to higher power consumption. |
| Maneuverability | Less maneuverable, requires runways for takeoff and landing. | Highly maneuverable, capable of vertical takeoff and landing (VTOL). |
| Payload Capacity | Potentially higher payload capacity for larger models. | Payload capacity varies greatly depending on size and design. |
| Cost | Generally more expensive than comparable multirotor drones. | Wide range of prices, from affordable hobbyist models to expensive professional systems. |
Specific Drone Model Examples
The DJI Mavic 3 boasts advanced camera capabilities and obstacle avoidance. The Autel Evo II series offers various camera options, including thermal imaging. The Parrot Anafi is known for its compact size and portability. Each model has unique operational features, such as flight modes, camera settings, and intelligent flight functions, that should be understood before operation.
Pre-Flight Checks and Procedures
A thorough pre-flight checklist is paramount for ensuring safe and legal drone operation. This involves checking the drone’s components, batteries, and regulatory compliance before each flight.
Pre-Flight Checklist
- Inspect the drone’s propellers, arms, and body for any damage.
- Check the battery level and ensure it is properly charged.
- Verify the GPS signal is strong and accurate.
- Confirm the controller is properly connected and calibrated.
- Review the flight plan and ensure it complies with local regulations.
- Check weather conditions and avoid flying in adverse weather.
- Inform relevant parties of your flight plans (if necessary).
Battery Checks and Charging
Always use the manufacturer-recommended charger and follow the instructions carefully. Never leave batteries unattended while charging. Inspect batteries regularly for any signs of damage or swelling. Proper battery care extends the lifespan and ensures safe operation.
Legal and Regulatory Requirements
Drone regulations vary significantly depending on location. It’s crucial to research and understand the specific rules and regulations in your area before flying. This includes obtaining necessary permits, registering your drone, and adhering to airspace restrictions. Failure to comply can result in fines or legal action.
Basic Drone Controls and Maneuvers
Understanding the drone controller and performing basic maneuvers are fundamental to safe drone operation. This section will explain the controller functions and guide you through essential maneuvers, including emergency landing procedures.
Drone Controller Functions
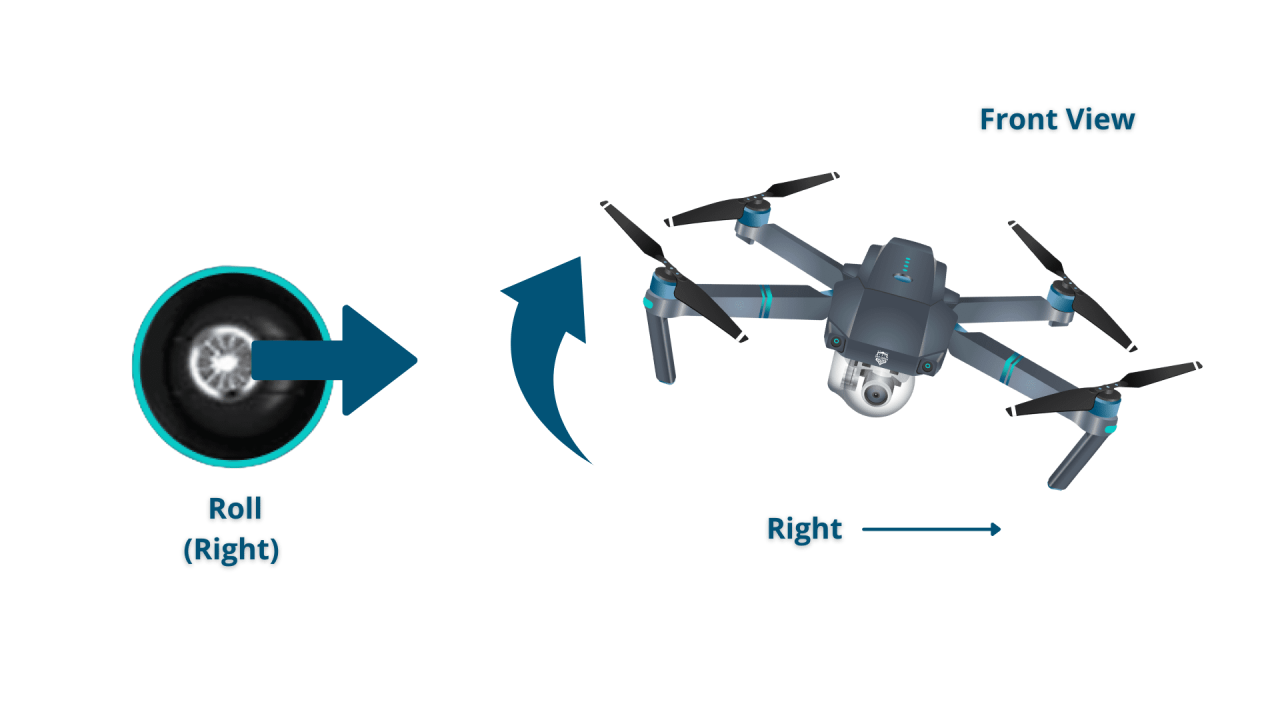
Most drone controllers have two joysticks. One joystick typically controls the drone’s altitude and yaw (rotation), while the other controls the drone’s forward/backward and left/right movement. Many controllers also have buttons for taking photos/videos, returning to home, and activating specific flight modes.
Basic Maneuvers
Taking off involves gently increasing the throttle. Landing is the reverse process, gradually decreasing the throttle until the drone gently touches down. Hovering requires maintaining a steady throttle and joystick inputs to maintain position. Moving in different directions involves manipulating the joysticks to control the drone’s movement.
Controlled Emergency Landing
- Immediately reduce throttle to initiate descent.
- Assess the surrounding environment to find a safe landing zone.
- Gently guide the drone towards the chosen landing zone, avoiding obstacles.
- Slowly reduce throttle until the drone lands gently.
- Power off the drone once it has landed safely.
Advanced Drone Techniques
This section will cover advanced techniques for precise flight control and achieving high-quality aerial shots, including different flight modes.
Precise Hovering and Stable Flight
Achieving precise hovering and stable flight in challenging conditions requires practice and understanding of wind effects. Adjusting the drone’s attitude and using features like Return-to-Home (RTH) can help mitigate these challenges. Experience and careful piloting are key to mastering these techniques.
Smooth Camera Movements and Stable Aerial Shots
Smooth camera movements require careful control of the drone’s movements and gimbal settings. Using cinematic flight modes and practicing smooth joystick movements can significantly improve the quality of aerial shots. Understanding the camera’s settings, such as shutter speed and ISO, is also crucial.
Flight Modes
GPS mode relies on satellite signals for positioning, providing stability and accurate flight. Attitude mode allows for more precise control, but requires more pilot skill and is more susceptible to wind. Understanding the differences between these and other flight modes is essential for adapting to different flight scenarios.
Drone Camera Operation and Image Capture: How To Operate A Drone
This section explains how to optimize your drone’s camera for high-quality aerial photography and videography.
Drone Camera Settings

Typical drone camera settings include aperture, shutter speed, ISO, and white balance. Understanding how these settings impact image quality is crucial for achieving desired results. Experimentation and understanding of photographic principles are key.
Optimal Image Exposure and White Balance
Achieving optimal exposure involves balancing the ISO, shutter speed, and aperture to capture well-exposed images. White balance adjusts the color temperature to ensure accurate color representation in various lighting conditions. Different lighting conditions require adjustments to these settings to avoid overexposed or underexposed images.
Workflow for High-Quality Aerial Media
A typical workflow involves pre-flight planning, including choosing the location, time of day, and desired shots. During the flight, maintain smooth movements and use appropriate camera settings. Post-processing can further enhance the quality of the captured media.
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource for this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone , which covers everything from pre-flight checks to advanced maneuvers. Mastering these skills ensures safe and responsible drone operation.
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance and troubleshooting are essential for ensuring the longevity and safe operation of your drone.
Routine Maintenance Schedule
- Inspect propellers for damage after each flight.
- Clean the drone body and camera lens regularly.
- Check all screws and connections for tightness.
- Store the drone in a cool, dry place.
- Perform a full inspection every few months.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Low battery can be addressed by charging the battery or using a spare battery. GPS signal loss can be resolved by finding an open area with a clear view of the sky. Motor malfunctions may require professional repair or replacement.
Safe Storage and Transportation
Store the drone in a protective case to prevent damage during transportation. Always transport the drone safely and securely to avoid accidental damage.
Safety Considerations and Best Practices
Safe and responsible drone operation requires awareness of airspace regulations and potential hazards.
Airspace Regulations and Restricted Areas
Always check for airspace restrictions before flying. Avoid flying near airports, military bases, or other restricted areas. Understanding and adhering to these regulations is crucial for safe and legal drone operation.
Potential Hazards and Mitigation
Potential hazards include collisions with obstacles, loss of control, and battery failure. Mitigation strategies include careful flight planning, maintaining visual line of sight, and using multiple batteries. Always prioritize safety.
Safety Guidelines for Responsible Drone Operation
- Always maintain visual line of sight with your drone.
- Never fly near people or crowds.
- Avoid flying in adverse weather conditions.
- Always respect privacy and avoid unauthorized surveillance.
- Fly responsibly and adhere to all applicable regulations.
Illustrative Examples of Drone Operations
Drones find applications across various fields, each with unique operational procedures and challenges.
Drone Applications, How to operate a drone
Aerial photography and videography use drones to capture stunning visuals from unique perspectives. Drone inspections involve using drones to inspect infrastructure, reducing risks and costs. Drone delivery utilizes drones for efficient and rapid delivery of goods, especially in remote areas. Each application requires specific operational procedures and considerations.
Operational Procedures and Challenges

Aerial photography requires careful planning of camera angles and lighting conditions. Inspections necessitate detailed flight plans to cover the entire area thoroughly. Delivery requires robust navigation systems and obstacle avoidance capabilities.
Camera Angles and Perspectives
Drones offer unique perspectives, such as high-angle shots showcasing the vastness of a landscape or low-angle shots emphasizing the scale of a structure. The ability to capture various angles and perspectives adds versatility and creative possibilities to many applications.
Mastering the art of drone operation is a rewarding journey that combines technical skill with responsible practice. This guide has provided a foundation in safe and effective drone piloting, from pre-flight preparation to advanced techniques. By adhering to the safety guidelines, legal regulations, and maintenance schedules Artikeld here, you can confidently explore the exciting possibilities of aerial perspectives and applications.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires practice and knowledge of regulations. For a comprehensive guide covering all aspects, including safety procedures and legal requirements, check out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone before your first flight. Safe and responsible drone operation is paramount for both personal safety and the integrity of airspace.
Remember that continuous learning and practice are key to becoming a proficient and responsible drone pilot.
Clarifying Questions
What is the maximum flight time for most consumer drones?
Flight times vary significantly depending on the drone model, battery size, and flight conditions (wind, payload). Expect anywhere from 15 to 30 minutes on a single battery charge for many popular consumer drones.
How do I register my drone?
Drone registration requirements vary by country and region. Check with your local aviation authority (e.g., the FAA in the USA) for specific regulations and registration procedures.
What happens if I lose the GPS signal during flight?
Most drones have fail-safe mechanisms, but losing GPS signal can lead to unpredictable behavior. Practice emergency landing procedures and be prepared to bring the drone down manually if GPS is lost.
What are the common causes of drone crashes?
Common causes include pilot error (inexperience, poor judgment), battery failure, mechanical malfunctions, and environmental factors (strong winds, obstacles).
